Backup & restore
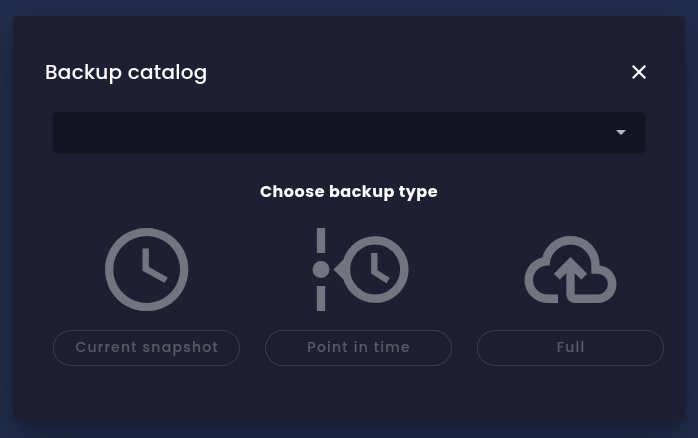 Backup options in evitaLab
Backup options in evitaLabNone of these backup options interferes with normal database operations; you can continue to read and write data while the backup is being created. Because of the append-only storage architecture, the backup process can run safely without blocking any operations. However, keep in mind that creating a backup may have some performance impact.
Current snapshot
The current snapshot contains a copy of the current data and, optionally, the contents of the transaction log (WAL), if you request that option when the backup is created. The contents of the transaction log are copied in full, and they may contain operations already reflected in the snapshot as well as operations that haven't been applied yet. When you restore data from such a backup, the snapshot is restored first, and then all unprocessed operations from the transaction log are applied in the order they were originally executed. This way, you can restore the database to the exact state it was in at the moment of backup creation. If you don't include the transaction log in the backup, the database is restored to the state it was in at the time of snapshot creation but might miss some unprocessed updates. The benefit of this approach is that a snapshot backup without WAL is the smallest possible backup you can create.
Point-in-time snapshot
You can include transaction log (WAL) files in the PIT snapshot backup as well, but this is intended only for debugging use cases. When you restore from a PIT snapshot that includes WAL files, the database is restored to the specified point in time, and then all operations from the included WAL files that were executed after that point are applied. You will end up with the current state of the database, just like with a current snapshot backup that includes WAL files.
Full file system copy
The full file system copy is the simplest way to back up the database. It copies and compresses the entire catalog storage directory, with files processed in the correct order. It might be quite large, but it contains all data, including historical data. When you restore from such a backup, the database is restored to the exact state it was in at the moment of backup creation. You can still perform PIT backups from a database restored this way, as all historical data is still present.


