Facet filtering
Faceted filtering, also known as parameterized filtering, is a user interface feature that allows users to refine search results by applying multiple filters based on various properties or "facets" like category, parameter, or brand. Users can toggle these filters on or off to drill down into a data set interactively, essentially performing real-time complex queries without technical knowledge. The benefits are twofold: First, it improves user experience by enabling more targeted and efficient searching. Second, it can increase conversion rates for e-commerce sites by helping users quickly find and purchase products that meet their specific criteria.
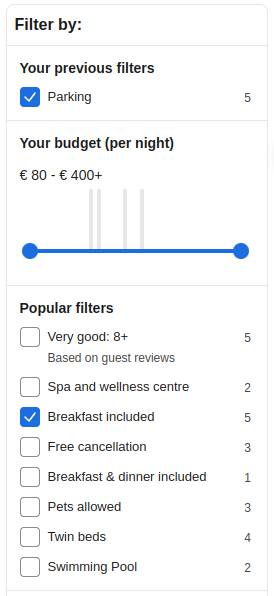 Facet filter example
Facet filter exampleThe key success factor of faceted search is to help users avoid situations where their filter combination returns no results. It works best when we gradually limit the facet options that don't make sense with the ones already selected, and also provide accurate, on-the-spot, real-time feedback about the number of results that will expand or limit the current selection when another facet is selected.
Facets are usually displayed as a list of checkboxes, radio buttons, drop-down menus, or sliders, and are organized into groups. The options within a group usually expand the current selection (logical disjunction), and the groups are usually combined with logical conjunction. Some of the facets can be negated (logical negation) to exclude results that match the facet option.
evitaLab visualization
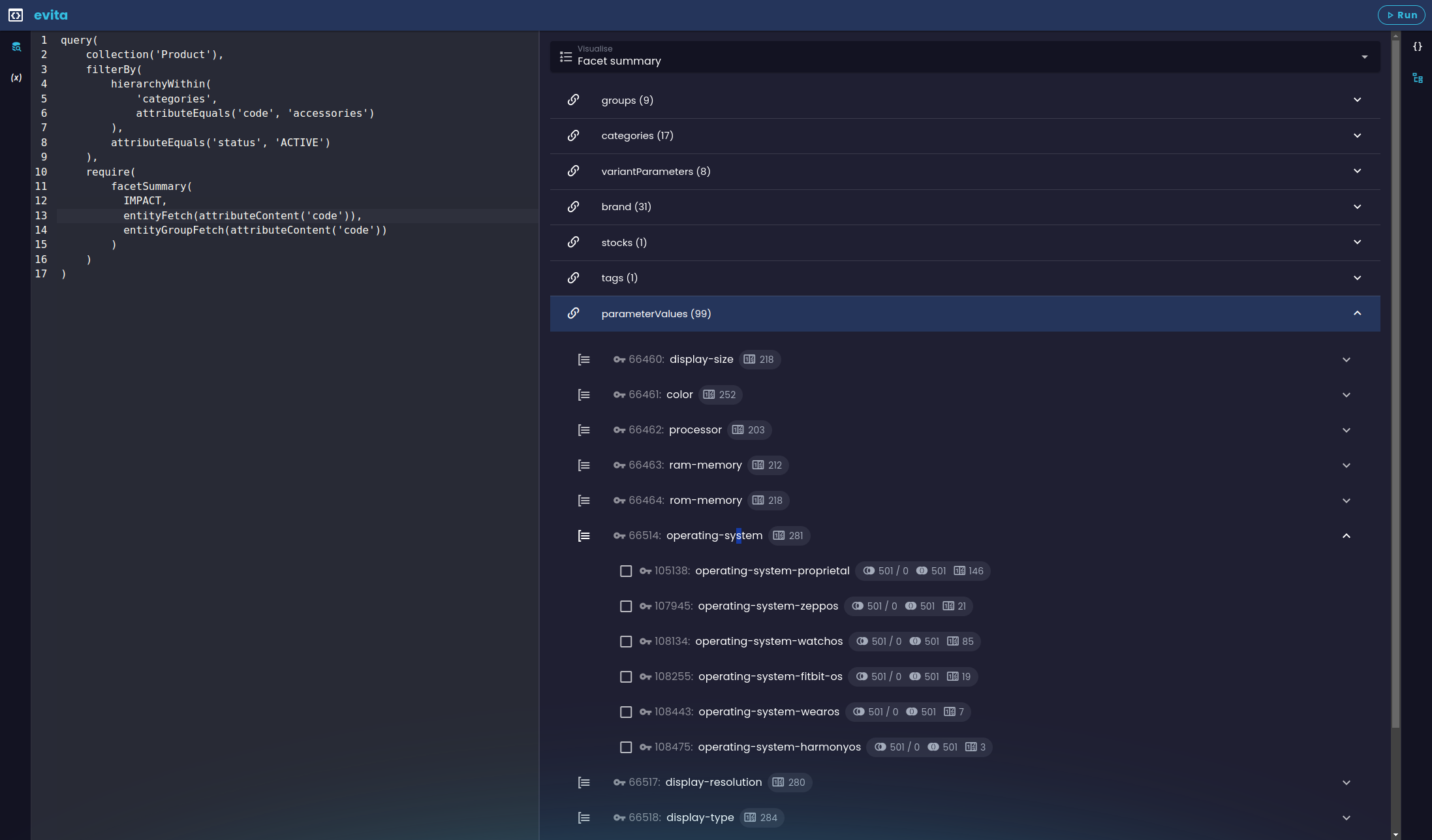 Facet summary visualization in the evitaLab console
Facet summary visualization in the evitaLab consoleThe visualization is organized in the same way as the facet summary itself:
| Icon | Meaning |
|---|---|
 | At the top level, you can see the links marked with the chain icon. |
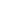 | Below them are the groups found within these reference types, marked with the group icon, and finally below the groups are the facet options themselves. |
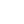 | Represents the number of entities returned that match this facet option when the user has no other facets selected (i.e., has an empty userFilter constraint). |
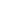 | Represents the current number of entities returned that match the filter constraints, next to the slash there is a difference in the number of results when this facet option is added to the user filter. |
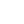 | Represents the total number of entities that will be displayed in the result when this facet option is selected (i.e., the number of entities that match the facet option in the entire dataset). ) |
Default facet calculation rules
- The facet summary is calculated only for entities that are returned in the current query result (excluding the effect of userFilter part of the query if present)
- The calculation respects any filter constraints placed outside the userFilter container.
- The default relation between facets within a group is logical disjunction (logical OR) unless you say otherwise.
- The default relation between facets in different groups / references is a logical conjuction (logical AND) unless you say otherwise.
Facet summary
- argument:enum(COUNTS|IMPACT)?
Default: COUNTS
optional argument of type
that allows you to specify the computation depth of the facet summary:- COUNTS: each facet contains the number of results that match the facet option only
- IMPACT: each non-selected facet contains the prediction of the number of results that would be returned if the facet option were selected (the impact analysis), this calculation is affected by the required constraints that change the default facet calculation behavior: conjunction, disjunction, negation.
- filterConstraint:filterBy
optional filter constraint that limits the facets displayed and calculated in the summary to those that match the specified filter constraint.
- filterConstraint:filterGroupBy
optional filter constraint that restricts the entire facet group whose facets are displayed and calculated in the summary to those that belong to the facet group matching the filter constraint.
- orderConstraint:orderBy
optional order constraint that specifies the order of the facet options within each facet group
- orderConstraint:orderGroupBy
optional order constraint that specifies the order of the facet groups
- requireConstraint:entityFetch
- optional requirement constraint that allows you to fetch the referenced entity body; the entityFetch constraint can contain nested referenceContent with an additional entityFetch / entityGroupFetch constraints that allows you to fetch the entities in a graph-like manner to an "infinite" depth
- requireConstraint:entityGroupFetch
- optional requirement constraint that allows you to fetch the referenced entity group body; the entityGroupFetch constraint can contain nested referenceContent with an additional entityFetch / entityGroupFetch constraints that allows you to fetch the entities in a graph-like manner to an "infinite" depth
Facet summary structure
The facet summary contains only entities referenced by entities returned in the current query response (excluding the effect of userFilter part of the query if present) and is organized in a three-tier structure:
- reference: the top-level contains the names of the references that are marked as faceted in the entity schema
- facet group: the second-level contains the groups that are specified in the returned entity's references
- facet: the third-level contains the facet options that represent entities of the returned entity's references
1st tier: reference
2nd tier: facet group
There may also be a special "group" for facets that are not related to a group.
3rd tier: facet
Facet contains the statistics for that facet option:
- count
It represents the number of all entities in the current query result (including user filter constraints) that have this facet (have reference to entity with this primary key).
- requested
- TRUE if this facet is requested in the user filter container of this query, FALSE otherwise (this property allows you to easily mark the facet checkbox as checked in the user interface).
- matchCount
- It represents the number of all entities that would match a new query derived from the current query if this particular facet option were selected (has reference to entity with this primary key). The current query is left intact, including the user filter part, but a new facet query is virtually added to the user filter to calculate the hypothetical impact of selecting the facet option.
- difference
- It represents the difference between the matchCount (hypothetical result should this facet be selected) and the current number of entities returned. It represents the size of the impact on the current result. It can be either positive (the facet option would expand the current result) or negative (the facet option would limit the current result). The difference can be 0 if the facet option doesn't change the current result.
- hasSense
- TRUE if the facet option combined with the current query still returns some results (matchCount > 0), FALSE otherwise. This property allows you to easily mark the facet checkbox as "disabled" in the user interface.
The query returns a list of "active" products in the "e-readers" category, and in the extra results index it also includes the facet summary calculation:
Fetching facet (group) bodies
Now you can see that the facet summary contains not only the primary keys, but also the somewhat comprehensible codes of the facets and their respective groups:
If you add the desired locale to the query and also list localized names, you'll get a result that's very close to the version you want to see in the user interface:
Filtering facet summary
We don't limit the search to a specific hierarchy because the filter is quite selective, as you can see in the result:
Ordering facet summary
Let's sort both facet groups and facets alphabetically by their English names:
You can see that the facet summary is now sorted where appropriate:
Facet summary of reference
- argument:string!
- mandatory argument specifying the name of the reference that is requested by this constraint, the reference must be marked as faceted in the entity schema
- argument:enum(COUNTS|IMPACT)
Default: COUNTS
optional argument of type
that allows you to specify the computation depth of the facet summary:- COUNTS: each facet contains the number of results that match the facet option only
- IMPACT: each non-selected facet contains the prediction of the number of results that would be returned if the facet option were selected (the impact analysis), this calculation is affected by the required constraints that change the default facet calculation behavior: conjunction, disjunction, negation.
- filterConstraint:filterBy
optional filter constraint that limits the facets displayed and calculated in the summary to those that match the specified filter constraint.
- filterConstraint:filterGroupBy
optional filter constraint that restricts the entire facet group whose facets are displayed and calculated in the summary to those that belong to the facet group matching the filter constraint.
- orderConstraint:orderBy
optional order constraint that specifies the order of the facet options within each facet group
- orderConstraint:orderGroupBy
optional order constraint that specifies the order of the facet groups
- optional requirement constraint that allows you to fetch the referenced entity body; the entityFetch constraint can contain nested referenceContent with an additional entityFetch / entityGroupFetch constraints that allows you to fetch the entities in a graph-like manner to an "infinite" depth
- requireConstraint:entityGroupFetch
- optional requirement constraint that allows you to fetch the referenced entity group body; the entityGroupFetch constraint can contain nested referenceContent with an additional entityFetch / entityGroupFetch constraints that allows you to fetch the entities in a graph-like manner to an "infinite" depth
As you can see, this is a fairly complex scenario that uses all the key features of the facet summary calculation:
Entity group fetch
Entity fetch
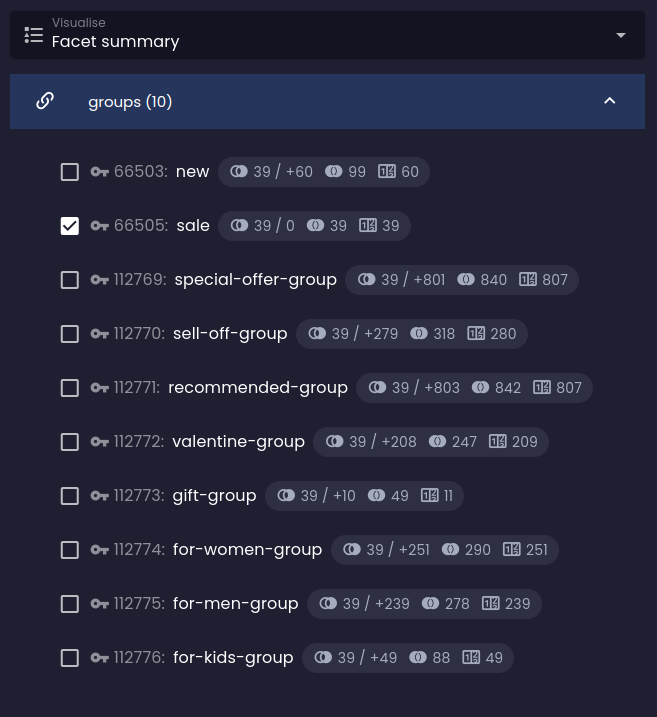
Facet groups conjunction
- argument:string!
- Mandatory argument specifying the name of the reference to which this constraint refers.
- argument:enum(WITH_DIFFERENT_FACETS_IN_GROUP|WITH_DIFFERENT_GROUPS)
Default: WITH_DIFFERENT_FACETS_IN_GROUP
Optional enumeration argument specifying whether the relationship type should be applied to facets at a particular level (within the same facet group, or to facets in different facet groups/references).
- filterConstraint:filterBy
Optional filter constraint that selects one or more facet groups whose facets will be combined with logical AND instead of the default logical OR.
If the filter is not defined, the behavior applies to all groups of a given reference in the facet summary.
| Default behaviour | Altered behaviour |
|---|---|
 Before Before | 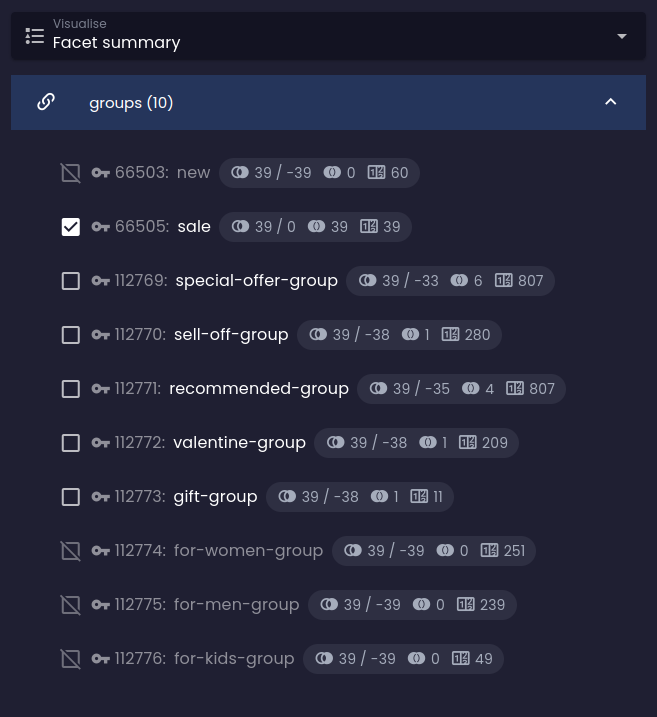 After After |
You can see that instead of increasing the number of results in the final set, the impact analysis predicts their reduction:
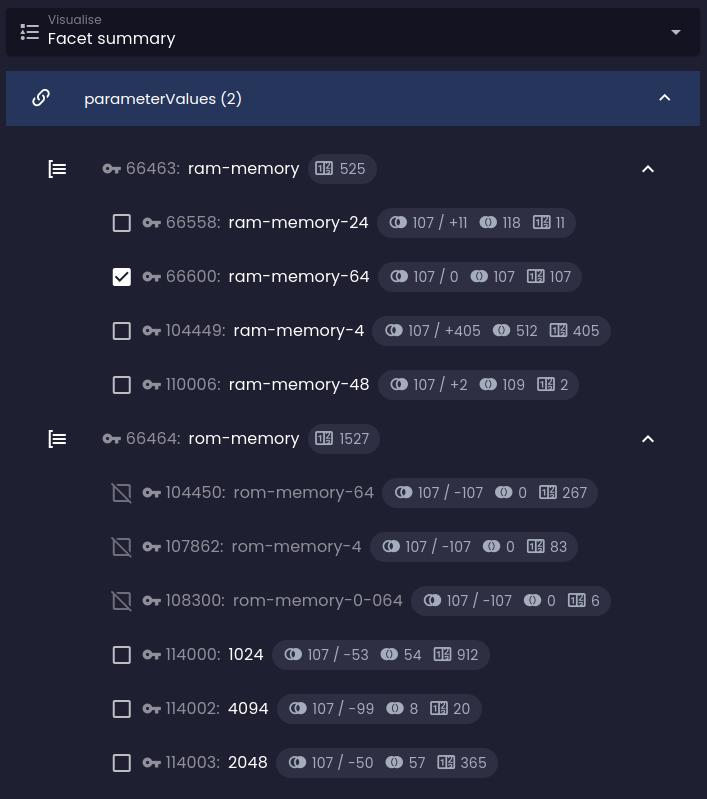
Facet groups disjunction
- argument:string!
- Mandatory argument specifying the name of the reference to which this constraint refers.
- argument:enum(WITH_DIFFERENT_FACETS_IN_GROUP|WITH_DIFFERENT_GROUPS)
Default: WITH_DIFFERENT_FACETS_IN_GROUP
Optional enumeration argument specifying whether the relationship type should be applied to facets at a particular level (within the same facet group, or to facets in different facet groups/references).
- filterConstraint:filterBy
Optional filter constraint that selects one or more facet groups whose facet options will be combined with logical disjunction (logical OR) with facets of different groups instead of the default logical conjunction (logical AND).
If the filter is not defined, the behavior applies to all groups of a given reference in the facet summary.
| Default behaviour | Altered behaviour |
|---|---|
 Before Before | 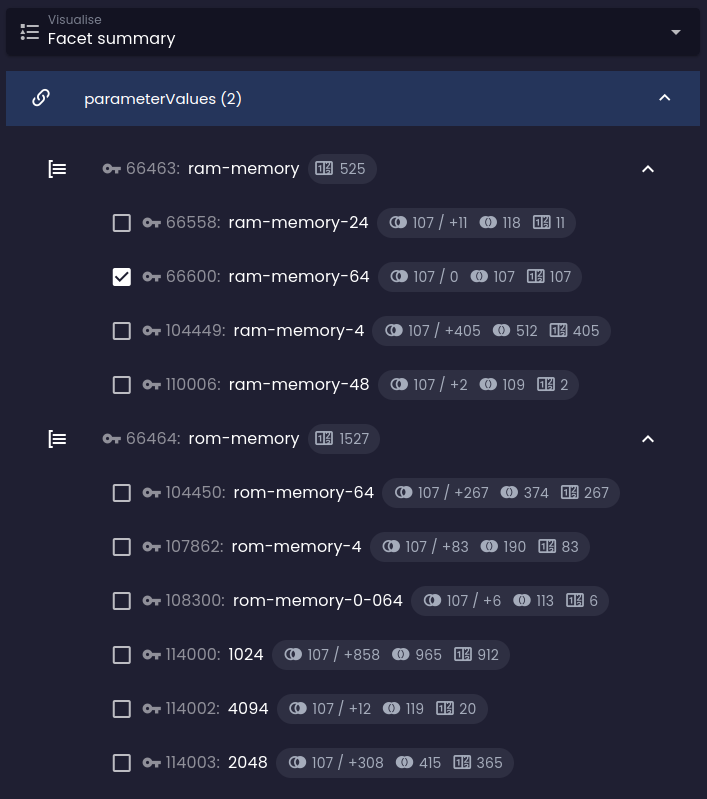 After After |
You can see that instead of reducing the number of results in the final set, the impact analysis predicts their expansion:
Facet groups negation
- argument:string!
- Mandatory argument specifying the name of the reference to which this constraint refers.
- argument:enum(WITH_DIFFERENT_FACETS_IN_GROUP|WITH_DIFFERENT_GROUPS)
Default: WITH_DIFFERENT_FACETS_IN_GROUP
Optional enumeration argument specifying whether the relationship type should be applied to facets at a particular level (within the same facet group, or to facets in different facet groups/references).
- filterConstraint:filterBy
Optional filter constraint that selects one or more facet groups whose facet options are negated. Thus, instead of returning only those items that reference that particular faceted entity, the query result will return only those items that don't reference it.
If the filter is not defined, the behavior applies to all groups of a particular reference in the facet summary.
| Default behaviour | Altered behaviour |
|---|---|
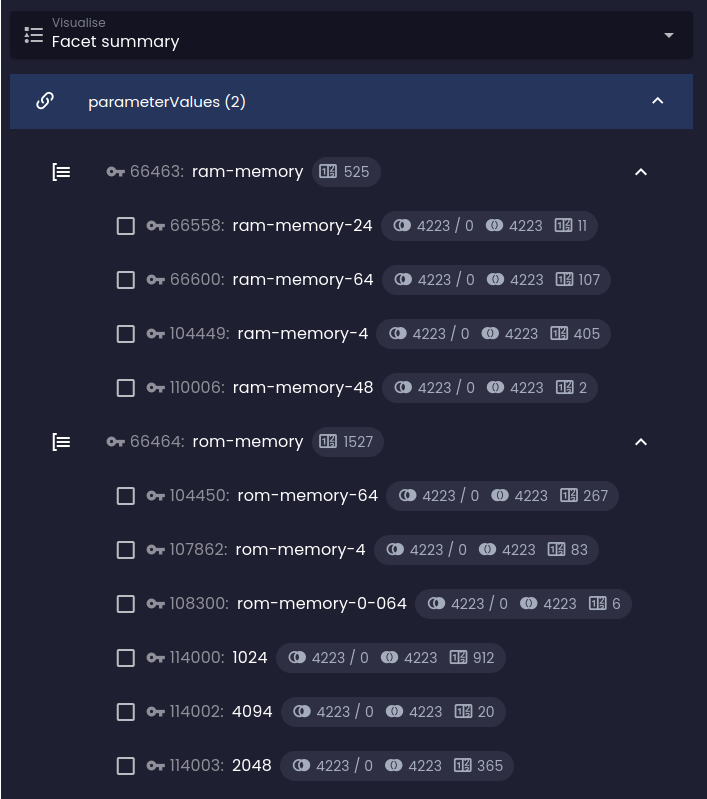 Before Before | 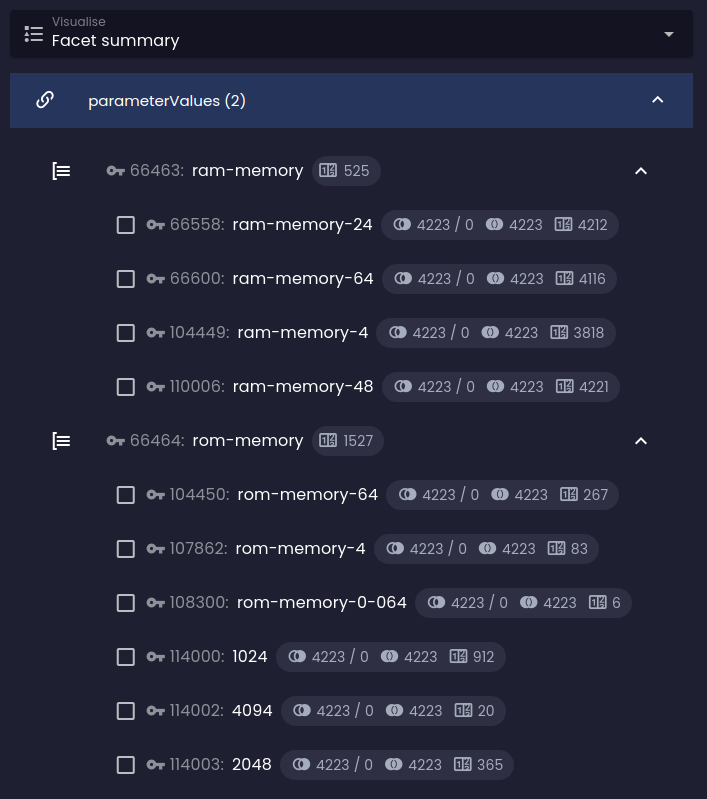 After After |
The predicted results in the negated groups are far greater than the numbers produced by the default behavior. As you can see, selecting any option in the RAM facet group predicts returning thousands of results, while the ROM facet group with default behavior predicts only a dozen of them:
Facet groups exclusivity
- argument:string!
- Mandatory argument specifying the name of the reference to which this constraint refers.
- argument:enum(WITH_DIFFERENT_FACETS_IN_GROUP|WITH_DIFFERENT_GROUPS)
Default: WITH_DIFFERENT_FACETS_IN_GROUP
Optional enumeration argument specifying whether the relationship type should be applied to facets at a particular level (within the same facet group, or to facets in different facet groups/references).
- filterConstraint:filterBy
Optional filter constraint that selects one or more facet groups whose facet options are mutually exclusive.
If the filter is not defined, the behavior applies to all groups of a particular reference in the facet summary.
Since this operator doesn't affect the actual result set output, it can only be used for the specific impact calculation, if you want to see the impact of selecting only one facet at a particular level.
| Default behaviour | Altered behaviour |
|---|---|
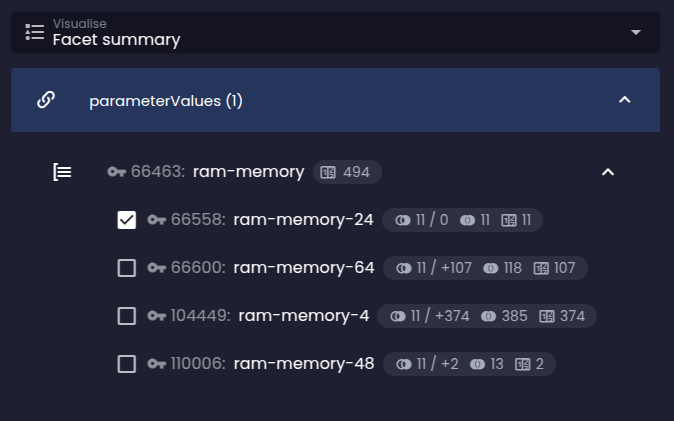 Before Before | 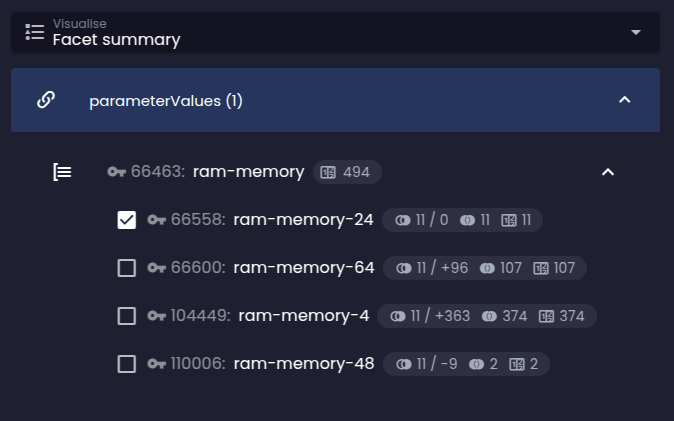 After After |
The predicted results in the exclusive groups are different for the numbers produced by the default behaviour when there is an existing facet selection used for the current query. As you can see, the current selection of the option in the RAM facet group doesn't affect the predicted counts (they remain the same as if no selection had been made):
Facet calculation rules
- argument:enum(DISJUNCTION|CONJUNCTION|NEGATION|EXCLUSIVITY)!
Mandatory argument specifying the default relationship behaviour for facets within the same facet group. You can change the default logical disjunction (logical OR) to a different value.
- argument:enum(DISJUNCTION|CONJUNCTION|NEGATION|EXCLUSIVITY)!
Mandatory argument specifying the default relationship behaviour for the facets between different facet groups or references. You can change the default logical operator (logical AND) to a different value.
- DISJUNCTION
Logical OR operator.
Effect on facet having behavior: entity will be present in the result set once it has at least one of the selected facets at a particular level (within the same facet group / between different groups).Effect on impact statistics: logical OR will likely extend the number of results in the final set.- CONJUNCTION
Logical AND operator.
Effect on facet having behavior: entity will be present in the result set once it has all the selected facets at a particular level (within the same facet group / between different groups).Effect on impact statistics: logical AND will likely reduce the number of results in the final set.- NEGATION
Logical AND NOT operator.
Effect on facet having behavior: entity will be present in the result set once it has none the selected facets at a particular level. As long as you leaf the other argument on system default it doesn't matter if you set NEGATION for the level within the same facet group or between different groups, because by the De Morgan's las the result will be the same (!a && !b is the equivalent to !(a || b)).Effect on impact statistics: logical AND NOT will likely extend the number of results in the final set if the entities have only a few facets of all the possible ones on average.- EXCLUSIVITY
Special logical operator that says that only one facet can be selected at a given level (within the same facet group / between different groups). This is useful for facets that are mutually exclusive.
Effect on facet having behaviour: none - it's up to the client to ensure that only one facet is selected at a given level. If the client provides more than one facet at a particular level, the system will use system defaults for the calculation (i.e. logical OR for facets within the same facet group and logical AND for facets between different groups).Effect on impact statistics: The calculated match count and impact will be calculated for the situation where only this particular facet is selected and no others in the same group / in different groups are selected.Note: since this operator doesn't affect the actual result set output, it can only be used for the specific impact calculation, if you want to see the impact of selecting only one facet at a particular level.
Changing the default facet calculation rules is similar to configuring each individual facet group relationship using requirement constraints:
The sample query that changes the default calculation rules is as follows


